Mabel Bent in exalted, not to say exhausted, company…
‘THIS is an age of plucky, strenuous women. They vie with men in the field of sport, they seek to invade his political kingdom, and they penetrate the remotest corners of the world in search of big game and fresh adventures in a manner which makes man stand amazed at their daring.’

A little research the other day (May 2020) turned up a fascinating, pre-Great War travel article in the Tatler for Wednesday, 30 November 1910 (no. 242, page 270) – and many thanks to the Illustrated London News/Mary Evans Picture Library, whose copyright it is, for allowing us to reproduce it here. It’s a tremendous, rare read. The author is one Joseph Heighton; forgive its title – ‘Pioneers in Petticoats’.
Twenty years or so either side of 1900, the journeys of Western women travellers were headline news – emancipatory, they very much reflected the times these women voyaged in, times every bit as challenging and frustrating for women as the tough terrain and hardships they fought through.

Mabel’s fortitude and abilities over the twenty years of explorations she undertook with Theodore Bent were indeed often written about, frequently on pages intended for women readers (some feature elsewhere in this archive).
The Tatler article is typical in its obvious admiration for Mabel, who has reached the age of 63, and has been travelling since she was a girl – most summers on the continent with her family, and then really taking metaphorical wing once she married (August 1877).
Here is what the Tatler has to say about Mabel:
“Asia Minor, Persia, Mashonaland, Abyssinia, Eastern Soudan, and South Arabia. These are some of the out-of-the-way corners of the globe which Mrs. Theodore Bent has penetrated when she accompanied her late husband on his archaeological expeditions. She has had several narrow escapes from death. In South Arabia she was nearly shot by bandits, while on another occasion she was ordered to dismount ‘in order that her throat might be cut’. Luckily better counsel prevailed with the would be murderers.”

Mabel would not be overshadowed by the company she keeps. And what exalted company it is – very much the great and the good of Western, or adopted Western, women travellers. Of course on one small page there must be notable omissions, e.g. the ubiquitous Isabella Bird (1831-1904), the Nile travellers Amelia Edwards (1831-1892) and Florence Baker (1841-1916), or fellow Egyptologists Marianne Brocklehurst and Mary Booth, both of whom Mabel knew. And the women featured are all English speakers: ‘Europeans’, such as Mabel’s nemesis, Jane Dieulafoy, are not included.
Also absent is the mysterious American Mabel refers to unkindly just as ‘Mrs. Phelps, a very fat American, in man’s attire’. The reference comes in Mabel’s diary entries for the couple’s amazing ride, south-north, the length of Persia in 1889: “They were all amazed indeed when they heard of our resolution to ride those 1300 miles or more ‘with a lady’, for not more than 3 ladies have done this before, and 2, Mme. Dieulafoy and Mrs. Phelps, a very fat American, in man’s attire. And as the days go on they are still more amazed at seeing me sitting serenely wondering what saddle I shall have.” (The Travel Chronicles of Mabel Bent, Vol 3, pages 27-8)
If anyone knows who this intrepid, if large, traveller is, then we would be fascinated to hear and give her recognition on this.
How well known to you are these ‘Pioneers in Petticoats’? Corona lockdown hours may well give you world enough and time to read up on them. A few notes are added here, courtesy of Wikipedia, to get you in the mood for travel…

The article begins with Mary Eliza Bakewell Gaunt (20 February 1861 – 19 January 1942), an Australian novelist with a taste for Africa.

Next to arrive is Barbara Freire-Marreco (1879–1967), an English anthropologist and folklorist. She was a member of the first class of anthropology students to graduate from Oxford in 1908.

Academically the most gifted, coming into focus now are Agnes Smith Lewis (1843–1926) and Margaret Dunlop Gibson (1843–1920), nées Agnes and Margaret Smith (sometimes referred to as the Westminster Sisters), were Semitic scholars. Born the twin daughters of John Smith of Irvine, Ayrshire, Scotland, they learned more than 12 languages between them, and became pioneers in their academic work, and benefactors to the Presbyterian Church of England, especially to Westminster College, Cambridge. Without our access to Wikipedia, Joseph Heighton gets it wrong in his line where he says Margaret Gibson is a friend, she is the twin sister; the girls were born four years or so before Mabel Bent.

Also high in academic esteem is Mary Henrietta Kingsley (13 October 1862 – 3 June 1900), English ethnographer, scientific writer, and explorer whose travels throughout West Africa and resulting work helped shape European perceptions of African cultures and British imperialism.

Again, it seems that Joseph Heighton was not quite right in saying that Charlotte Mansfield (1881-1936), English novelist, poet, and traveller, completed Rhodes’ dream tour of the Cape to Cairo; she made it as far as Lake Tanganyika, good going nevertheless (see Mary Hall a little later).

Mary French Sheldon (May 10, 1847 – 1936), as author May French Sheldon, was an American author and explorer. Born the same year as Mabel Bent (and they, indeed, knew each other, see below), she was made a fellow of the Royal Geographical Society, among the first fifteen women to receive this honour, in November 1892. (Mabel Bent was in line for the next group of women Fellows, but the privilege was shamefully withdrawn and women Fellows were not elected again until 1913.)

Mary Hall (1857-1912) really did make the trip from Cape to Cairo (see Charlotte Mansfield above). Her book A Woman’s Trek from the Cape to Cairo (1907) is available online. After Africa, Mary switched to Australia and the Far East; it seems her adventures there were published posthumously (A Woman in the Antipodes and in the Far East, c. 1914).

Our caravan of great women travellers continues, after the heat of Australia, in the ice of the Arctic with Josephine Cecilia Diebitsch Peary (May 22, 1863 – December 19, 1955), an American author and Arctic explorer of renown.

We know, at least, that Mabel and May French Sheldon (see above) were acquaintances, if not friends. The Belfast Telegraph of Saturday, 27 June 1908 informs us that “Mrs Theodore Bent was ‘at home’ recently to some 200 of her friends, when a very enjoyable evening was spent in the beautiful suite of rooms in her house in Great Cumberland Place, that are much more interesting than many museums, as they are full of the most wonderful curios brought back by Mrs Bent from Persia, Russia, Norway, the Soudan, the Holy Land, and the many other parts of the world in which she has travelled and explored. The hostess, handsomely dressed in mauve, with white lace and many diamonds, received her guests at the entrance to the principal drawing-room, and near her stood her sister, Mrs Bagenal, dressed in black and silver, who had come over from her place in Co. Carlow for this and other functions of the season; and amongst other invited guests were …. Mrs French Seldon, etc., etc.”

Another acquaintance was Mary Brodrick (1858-1933), one of the first female excavators in Egypt. Wikipedia mentions a description from the Daily Mail (1906) noting her as ‘perhaps the greatest lady Egyptologist of the day’. From Mabel’s diaries we have two direct references to her:
- December 1895: “We have been to the museum twice, and to lunch with Professor Sayce on the ‘dahabeya’, which is his charming home, and have been asked by Miss Brodrick, an Egyptologist lady, to tea on hers on Thursday…” [Travel Chronicles of Mrs J Theodore Bent, Vol 2, Oxford, 2012, p.225]
- Sunday 6th, February 1898: “I walked by land to church in the hotel with a funny old American woman, Mrs. Austin. Professor Sayce preached a beautiful sermon. The chaplain is Mr. [left blank]. Coming out I was hailed by Miss Brodrick, who edited ‘Murray’, and she asked me to tea on the ‘Alma’. Her chum, Miss Morton, was with her – also 2 others, Miss Dickson and Miss Kilburn. I also dined with them. We rowed round Elephantine. Professor Sayce had taken me over it. His dahabeya was off to Luxor…” [Travel Chronicles of Mrs J Theodore Bent, Vol 2, Oxford, 2012, p.270]
Of course, there is a library of literature now available on women travellers. A workable summary is provided by Tracey Jean Boisseau for her contribution under the heading ‘Explorers and Exploration’ in The Oxford Encyclopedia of Women in World History, Volume 1, 2008, pages 227-231.
Now and then in the pages below we will add notable references to Mabel that appeared in other contemporary magazines of a general nature.
One such is an article in The Liverpool Weekly Courier, for Saturday, 9 December, 1893. The Courier picked it up from Hearth and Home of 2 November 1893 (Bent being a well-known name in Liverpool – Theodore’s uncle being Lord Mayor in the 1850s). The Bents had been circulating a press release announcing their forthcoming expedition to ‘South Arabia’ and, as ever, Mabel’s participation aroused interest:

“One of the most interesting collections in the British Museum is that contributed by Mr. and Mrs. Theodore Bent, who, after having explored almost every known portion of the globe, are still, like Alexander, sighing for fresh regions to conquer. Of recent years, women have shown much intrepidity as travellers, as witness the peregrinations of Lady Baker [See above: Barbara Maria Szasz, 1841-1916, Hungarian-born British explorer], the indomitable fortitude of Lady Burton [Isabel Burton, née Arundell, 1831-1896, English writer, explorer and adventurer], and the wonderful resourcefulness of Mrs. French Sheldon [See above: Mary French Sheldon, 1847-1936, American explorer], who, capable authoress as she is, abandoned the field of literature temporarily for a lonely wander through the Dark Continent, and who came out smiling with such staggering, yet solid, stories that incredulity retired baffled and only admiration remained. In the same way Mrs. Theodore Bent has penetrated unknown and barbarous regions until to hear her tales of adventures is like listening to one of Ballantyne’s [R. M. Ballantyne, 1825-1894, Scottish author] or Henty’s [G. A. Henty, 1832-1902, English novelist and war correspondent] delightful books. Next week we see her depart, accompanied by her husband, to explore South Arabia, whence they will return, all being well, in March or April. There must be a great deal to see and write about in this little travelled part of the earth’s surface, and one may depend on it that whatever is interesting will be retailed to their countrymen on their return by this remarkable couple. An exhaustive medicine chest will be a feature of the impedimenta, and it may be interesting to ladies to know that Mrs. Bent’s only wear is serviceable serge.”
An account of Mabel at Great Zimbabwe features in Sarah Tooley’s long article on famous women travellers that appeared in Lady’s Realm (Vol. 1, Nov. 1896 – April 1897, pp. 480 ff). It makes poignant reading in that the article was being compiled and published as the Bents were desperately ill in Aden. The journal’s end date is April 1897, a few weeks later and Theodore is dead:
“In Mrs. Theodore Bent we have a traveller who has made South Africa a special field for exploration. Mrs. Bent had, with her husband, already done considerable travel in Persia, Asia Minor, and the Greek Islands, when, in 1891, she started for a still more adventurous journey in Africa. Although doubt was expressed as the advisability of her accompanying the expedition, she proved to be the only one of the party who escaped fever; she did not, indeed, have a day’s illness throughout the whole of the year spent in African travel.
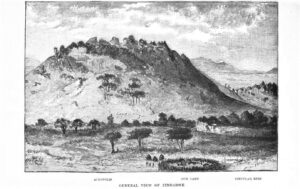
“Mrs. Bent is a lady of great learning and knowledge, as well as being a distinguished traveller, and has rendered valuable assistance to her husband in the preparation of his various books; and she is also a skilled photographer. The expedition to South Africa, which was taken under the auspices of the Royal Geographical Society, the Chartered Company, and the British Association, was for the purpose of the exploration and excavation of those ancient massive and mysterious ruins which exist in Mashonaland and which point to a time when the country of Lobengula and his indunas was a centre of wealth and civilization, with cities, palaces, and temples.
“Mrs. Bent had quite a romantic camp life when working amongst the ruins of Zimbabwe. Two waggons served the expedition as bedrooms; an Indian terrace, constructed of grass and sticks, made a novel and charming dining-room; a tent formed the drawing-room; and the suite were decorated by Mrs. Bent with a wealth of brilliant flowers which no conservatory at home could have supplied. She also had a dark tent for photography, and improvised kitchen, and a poultry-house. A hedge of grass surrounded the whole, and gave a picturesque finish to the camp. Outside this royal domain were the huts for the native workmen. Alas! however, for the delights of gypsy life. One day the long grass of the veldt started into flames, which, lashed to fury by the wind, came within a few yards of the camp, and were only beaten back by frantic efforts on the part of the little colony; the small huts were, indeed, burnt to ashes.
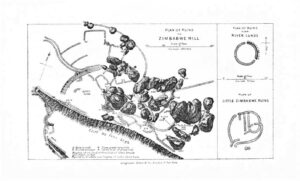
“A year was spent by Mr. and Mrs. Bent in South Africa studying the ruins and the people, the result of their investigations, in which they were assisted by Mr. R.M.W. Swan, being told in that delightful book, “The Ruined Cities of Mashonaland”. They come to the conclusion that the land, since rendered famous by the Jameson expedition, may revive the glories of the ancient ruins under British occupation and development. Mr. and Mrs. Bent are systematic travellers, and each year sees them set out for some distant land, although they usually spend the season in town, where their house in Upper Cumberland Place [sic], which is filed with mementoes of their journeys, is the resort of many famous and learned people.”
A further good example of Mabel’s abilities can be found in her very last adventure with Theodore, on Sokotra in early 1897. When their guides tried to persuade them to take a boat to avoid a particularly treacherous path (to the locals’ financial benefit), the adventurer writes: “We assured them that we had landed in Sokotra… to see the island, and not to circumnavigate it. Others could pass, so we could. Their last hope was in my hoped-for faintheartedness. They watched till I was alone in the tent, and, having recounted all the perils over again, said: ‘Let the men go over the mountain, but you, Bibi! will go in a boat, safely. You cannot climb, you cannot ride the camel, no one can hold you; the path is too narrow, and you will be afraid.’” The guides, obviously, did not know Mabel Bent. (Extract from Southern Arabia, 1900, p.368)

Interestingly, just down the road at number 28 Great Cumberland Place (Mabel rented no. 13) lived, from 1928, the equally, if not more so, adventurous traveller in Arabia and elsewhere, Joan ‘Rosita’ Forbes (1890-1967). Her 1925 book (New York, pp. 348-9), From Red Sea To Blue Nile – Abyssinian Adventure contains some references to the Bents at Axum, Ethiopia, but we don’t know whether Rosita ever made contact with the elderly Mabel Bent in the few months they were near neighbours; both women travelled many thousands of miles, but that mere 100 metres or so that separated them may well have been steps too far…

A little space must be dedicated also to Amice Calverley (1896–1959), the English-born Canadian Egyptologist who was instrumental in the recording and publication of the decoration scheme within the temple of King Sethos I at Abydos. As an associate of the Egyptian Exploration Society in 1927, there is a chance that she was known to Mabel Bent, who was in the final years of her life. Mabel celebrated her 38th birthday (1885) atop one of the Gizeh pyramids. The Bents visited Egypt several times; Mabel travelled there alone in 1898, the year after Theodore’s death.

No list of indomitable women travellers would be complete without a reference to the incredible Ida Laura Pfeiffer, in whose footprints Mabel occasionally followed. Although the latter never refers directly to the Austrian globetrotter in her diaries, Mabel would certainly have known of her, and probably read Ida’s travel accounts, several of which were already translated into English in her time. Ida died when Mabel Hall-Dare was just a girl of ten or so in the south of Ireland.
Any bibliography on notable women travellers would include ‘The Women Who Did’, Chapter 3, in Archaeologists in Print by Amara Thornton, UCL press, 2018, pp.48-74.
 Leave a comment or contact us about this article
Leave a comment or contact us about this article